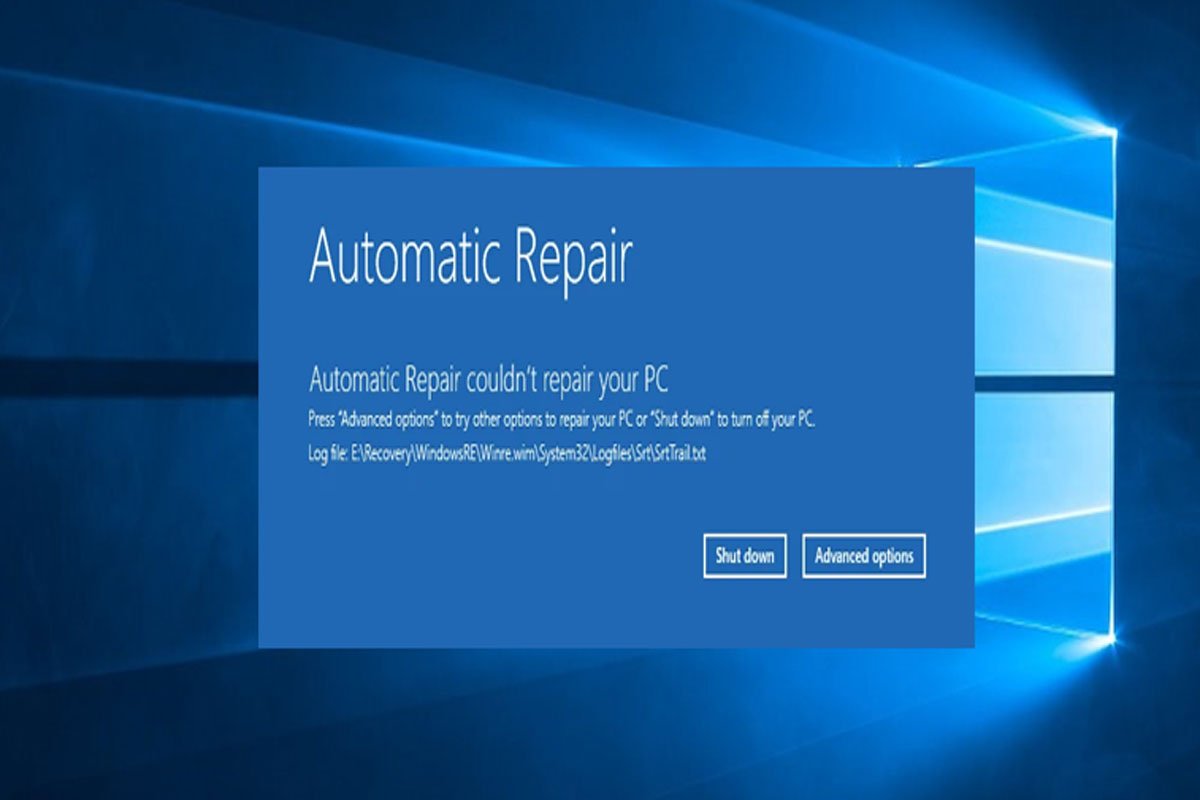
In general, Windows 11 is a stable operating system. Sometimes it can really get under your skin when you get a SrtTrail.txt BSOD error. Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system already contains an automatic repair tool. In general, this helps to resolve all start-up issues. But, sometimes, users may not be able to fix it on their own. Well, that’s the reason why we are here. In this guide, you will learn how to fix the SrtTrial.txt BSOD error. So, let’s get started with the guide.
What is the srttrail.txt Error?
If Windows is stuck on boot, the srttrail.txt file will continue to appear as a log of all the times it failed to boot properly.
It appears mostly during boot-up, but it can also appear while Windows is running. On the screen, you have two options: either shut down or use the “Advanced options.” Well, it is still unclear why this error message occurs. But here are some of the most common causes:
- Incompatible hardware (corrupted drivers, etc.)
- Malware or virus
- A corrupted program is installed
- Virus-infected system files
- Corrupted Windows registry
- A damaged or corrupted Windows Boot Manager file
Top Ways to Fix Srttrail.txt BSOD Error in Windows 11
If you are facing this problem, you must perform these fixes to resolve the SrtTrial.txt BSOD error:
Fix 1: Perform A System Restore
You may experience several restarts while your computer tries to fix the srttrail.txt error. The blue screen with boot options will appear once the restarts stop. You can restore your system to a previous system restore point by following the steps below on reaching the screen.
- To access advanced boot options, click Troubleshoot in the boot options.
- Choose the option for system restore on the current screen.
- Enter the administrator’s credentials if necessary.
- Click Next if you want to use the current restore point. Alternatively, click on “Choose another restore point” and then click Next.
- When the restore point is chosen, the computer begins restoring the system.
Fix 2: Disable Automatic Startup Repair
One of the easiest ways to resolve srttrail.txt issues is to disable automatic startup repair. It is possible to turn off the automatic repair by using the “bcedit” command provided by Windows.


- It may take some time for the process to complete. After it’s done, restart your computer.
Fix 3: Disconnect Your USB Devices
Ensure that all peripheral devices, such as printers, USB devices, cameras, and other non-essential devices, are disconnected. Afterward, restart your computer to see if the problem still persists. If you do not receive the error message, then you have a problem with one of these devices (with its drivers). To find out what is causing the problem, try reconnecting the peripherals one by one and restarting your computer. You will have to update the driver once the malfunctioning device is identified. It is likely that you will need to repair or replace the peripherals if the driver update doesn’t work.
Fix 4: Run the Command Prompt from the Windows 11 Boot Options Menu
Here are some commands you can run using the Command Prompt to fix the error:
- You need to copy and paste the first one into the window and press Enter. Then, repeat the process for the other two.
Fix 5: Scan the System for Malware
Virus and malware infestations are the most common cause of Srttrail.txt and can only be rooted out in Safe Mode by running a full scan. Here’s how to do it:
- Go to Advanced options on the error screen.
- Select Startup settings.
- Then click on Restart.
- To enable Safe Mode, press 4.
- Press Start, type Windows Security, and open it in Safe Mode.
- In the left pane, click Scan options under Virus & Threat Protection.
- Choose Full Scan.
- Finally, click on Scan Now at the bottom of the page.
Fix 6: Run SFC and Check Disk (CHKDSK) Command
You can repair corrupted system files by running the System File Checker and Check Disk utilities. Follow these steps to do so:
- Select Advanced options.
- Next, open the Command Prompt window.
- Type the following command at the command prompt: sfc /scannow


- After that, press Enter. Let the scan finish.
- For the repair changes to take effect, close the command prompt and restart your PC.
- To check the drive, open the Command prompt (as shown earlier) and type: chkdsk /f /r /x C:


- Press Enter.
Fix 7: Reset Your PC
When all other methods have failed to fix your PC’s issue, resetting it is the last resort. It’s good to know that your personal files and folders will not be lost. If you reset your PC, you will be able to remove all the programs you’ve installed, and all the settings will be reset to their defaults.
- When it comes to resetting your PC, you must enter the Recovery mode, as discussed earlier in this guide, and click ‘Troubleshoot.’
- On the troubleshooting screen, click ‘Reset this PC‘.


- Depending on your preference, you can keep your files but only remove the apps and settings or restore the device back to factory settings. Choose your preferred option. Here, I’m choosing ‘Remove everything,’ but the choice is ultimately yours.


- To install Windows using Microsoft servers, click the ‘Cloud download‘ tile. If your computer already has the files to install Windows, you can also choose ‘Local reinstall.’


- Choose whether to remove files only from the Windows installer drive or from all drives on the next screen. However, if you only want to wipe the drive where Windows is installed, click the ‘Only the drive where Windows is installed‘ option. To remove files from all your drives, choose ‘All drives.’


- To delete your files, click on the ‘Just remove my files‘ option. If you are giving your machine away, select ‘Fully clean the drive.’


- Depending on your Windows machine, it might take a few minutes for everything to be ready. To start the process, click on the ‘Reset‘ button located in the bottom right corner.